

Net Metering
Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy producer (Prosumer) for the electricity they add to the grid, but no payment will be made for the excess electricity supplied over the consumption under this scheme. For example, if the solar PV system produces more energy (kwh) than the consumption in a particular month, this excess energy flows to the grid, which is called banking. This banked energy can be used by that prosumer throughout a maximum of ten years period. If the consumption is greater than the energy produced in a particular month, the electricity bill will be calculated for the net energy imported(used) during the period.
Net Accounting
The Net Accounting Scheme is a program that allows the prosumer to export electricity produced through their solar PV systems to the national grid. The connection configuration is the same as the net metering scheme, the only difference is the prosumer will be paid for the excess energy exported to the grid. The applicable paying amount (Feed-in Tariff) per unit (kWh) will be one of the Cabinet approved tariffs (Please see below the approved tariffs) which will be mutually agreed by both parties at the time of signing the agreement.
Net Plus
This involves getting paid for all the amount of electricity generated using the solar panels fixed on the premises. There is no link between the amount of energy used by the prosumer and the amount of energy produced by the system. Two separate meters will be installed to measure import and export of energy separately. The prosumer is responsible for settling their electricity bill in accordance with the prevailing end-user tariff rates. Conversely, the utility provider (CEB/LECO) reimburse the prosumer based on the payment methodology approved by the cabinet, which was mutually agreed by both parties at the time of signing the agreement.
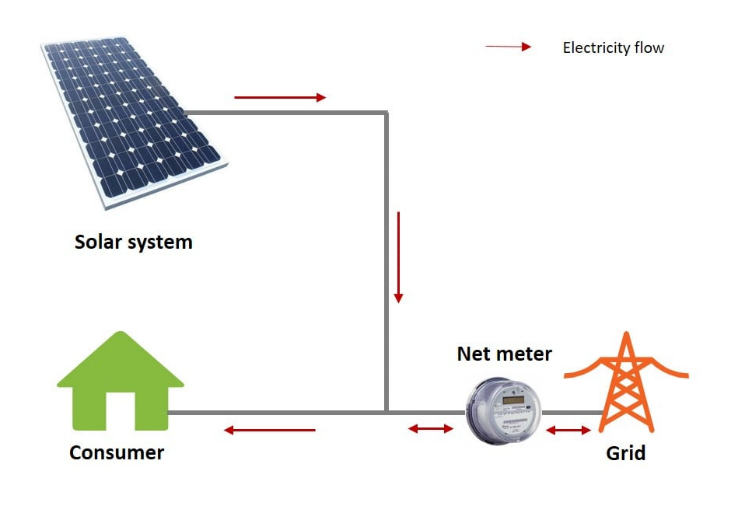
Figure 1: Net metering and Net Accounting
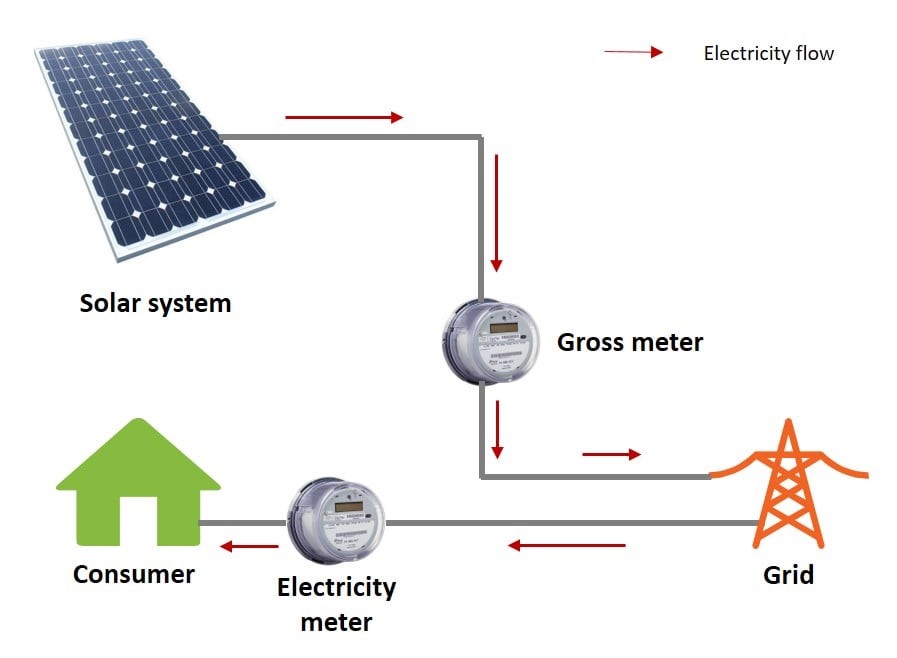
Figure 2: How works Net Plus
NET PLUS PLUS
Currently, all other schemes connected to the grid are limited to the customer’s contract demand. This limitation results in the underutilization of available roof space for solar power generation beyond the contracted demand. To address this issue, the utility has introduced the Net Plus Plus scheme, which allows prosumers to install Rooftop Solar PV systems beyond their contract demand.
Under the Net Plus Plus scheme, the Rooftop Solar PV system is classified as a power plant, and prosumers are permitted to consume only the auxiliary power required for system operation. Existing consumers can leverage the Net Plus Plus scheme to generate and supply excess electricity to the grid using their additional roof space. An essential aspect of the Net Plus Plus scheme is the separation of its wiring from all other internal wiring systems.
The Net Plus Plus scheme facilitates the implementation of a roof rental or aggregator model, which aims to maximize rooftop solar generation. Under this model, investors or tariff customers can enter into agreements with the utility. The interconnection agreement closely resembles that of the Net Plus scheme, and the payment structure aligns with other existing schemes.
Tariff before October 2022
As with the previous tariff system (not used at present) the excess will be paid as rate of Rs.22.00 per unit during the first 07 years and from the 8th year onwards at the rate of Rs.15.50 per unit by the Utility Provider.
Fixed Flat Tariff from 26th October 2022 to 1st July 2024
Approved date 2022-10-26
| Capacity (kW, AC) | Applicable flat tariff for 20 years agreement period (LKR) |
| Up to 500 | 37.00 |
| More than 500 | 34.50 |
| Solar aggregation Schemes | 34.50 |
Fixed Flat Tariff from 1st July 2024
| Capacity (kW, AC) | Applicable flat tariff for 20 years agreement period (LKR. /kWh) |
|
Up to 500 |
27.06 |
| More than 500 | 23.18 |
| Aggregation schemes | 23.18 |
Tariff Announcement for Rooftop Solar PV (RTSPV) Systems (Source: CEB)
Approved date 26 June 2023. More details will be published later.
Read more: Environment and Renewable Energy | PUCSL